Inguinal Hernia In Children. Between 12 to 14 weeks of fetal development the testicles or ovaries form in the abdomen. Accordingly surgical repair of a symptomatic inguinal. Over 99 of inguinal hernias in children are indirect. In infants and young children the risk of incarceration of the unrepaired inguinal hernia is as high as 31 usually in the first few months of life posing a significant risk to the bowel and testicle.

Failure of closure of the processus vaginalis accounts for nearly all the inguino scrotal abnormalities seen in infancy and childhood. The hernia may contain fluid tissue from the abdomen or part of an organ such as an intestine. Babies born early or who have a family history of hernias are more likely to develop. What is a Pediatric Inguinal Hernia Groin. Article in French Sebastiani M Giacchi R Rossi M Lungarotti F. Most inguinal hernias in infants and children are indirect due to patent processus vaginalis.
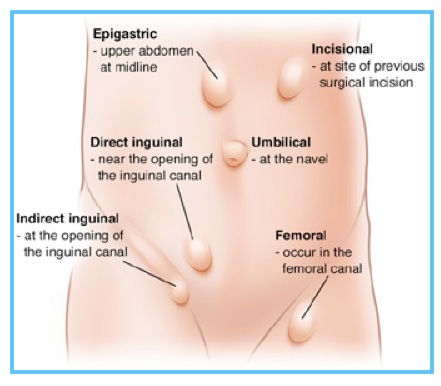
What is an inguinal hernia.
Failure of closure of the processus vaginalis accounts for nearly all the inguino scrotal abnormalities seen in infancy and childhood. However there may be benefits of delaying surgery in individual cases. Inguinal hernias in children result from a weakness in the abdominal wall that is present at birth. Treatment for inguinal hernia. The bulge in the groin might only be noticed when the child is crying coughing or straining during a bowel movement or it might appear to be larger during these times. This is called an inguinal hernia.